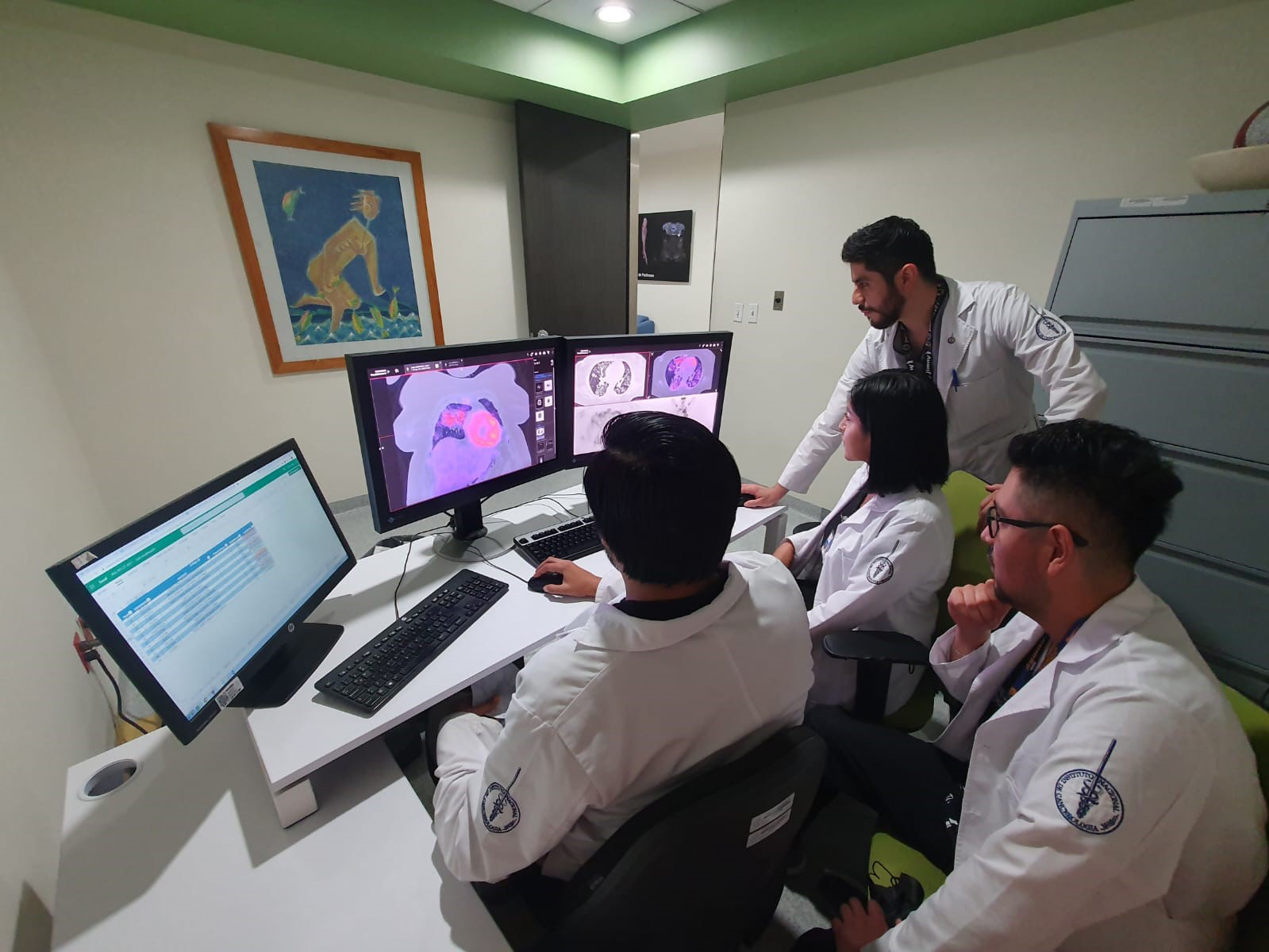
Every year, around 2.6 billion people are affected by diseases originating in animals (zoonotic diseases). To prevent pandemics, it is essential to detect and characterize zoonotic diseases before an outbreak occurs, or at an early stage.
As part of the IAEA’s Zoonotic Disease Integrated Action (ZODIAC) initiative launched in 2020, the ZODIAC Respiratory Disease Phenotype Observatory will create a secure medical imaging repository to foster global cooperation on large scale data analysis of disease patterns, enabling the early detection of zoonotic diseases that could potentially cause pandemics.
The observatory will use artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning and deep learning, to identify the patterns of respiratory diseases such as Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), COVID-19 and pneumonia and detect the emergence of new variants.
“The IAEA’s ZODIAC Respiratory Disease Phenotype Observatory will play an important role in identifying the emergence of new infectious diseases around the world, monitoring their spread and facilitating the rapid development of AI models for treatment support,” said Professor Georg Langs, Head of the Computational Imaging Research Lab at the Medical University of Vienna, one of the project’s core laboratories. “Because it works with research institutions across the globe, the observatory will be able to analyse a much larger and more demographically diverse collection of data on respiratory diseases than previous studies.”